Loading Generic Array Data¶
Even if your data is not strictly related to fields commonly used in astrophysical codes or your code is not supported yet, you can still feed it to yt to use its advanced visualization and analysis facilities. The only requirement is that your data can be represented as three-dimensional NumPy arrays with a consistent grid structure. What follows are some common examples of loading in generic array data that you may find useful.
Generic Unigrid Data¶
The simplest case is that of a single grid of data spanning the domain, with one or more fields. The data could be generated from a variety of sources; we’ll just give three common examples:
Data generated “on-the-fly”¶
The most common example is that of data that is generated in memory from the currently running script or notebook.
[1]:
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import default_rng # we'll be generating random numbers here
import yt
prng = default_rng(seed=42)
In this example, we’ll just create a 3-D array of random floating-point data using NumPy:
[2]:
arr = prng.random(size=(64, 64, 64))
To load this data into yt, we need associate it with a field. The data dictionary consists of one or more fields, each consisting of a tuple of a NumPy array and a unit string. Then, we can call load_uniform_grid:
[3]:
data = {"density": (arr, "g/cm**3")}
bbox = np.array([[-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5]])
ds = yt.load_uniform_grid(data, arr.shape, length_unit="Mpc", bbox=bbox, nprocs=64)
load_uniform_grid takes the following arguments and optional keywords:
data: This is a dict of numpy arrays, where the keys are the field namesdomain_dimensions: The domain dimensions of the unigridlength_unit: The unit that corresponds tocode_length, can be a string, tuple, or floating-point numberbbox: Size of computational domain in units ofcode_lengthnprocs: If greater than 1, will create this number of subarrays out of datasim_time: The simulation time in secondsmass_unit: The unit that corresponds tocode_mass, can be a string, tuple, or floating-point numbertime_unit: The unit that corresponds tocode_time, can be a string, tuple, or floating-point numbervelocity_unit: The unit that corresponds tocode_velocitymagnetic_unit: The unit that corresponds tocode_magnetic, i.e. the internal units used to represent magnetic field strengths. NOTE: if you want magnetic field units to be in the SI unit system, you must specify it here, e.g.magnetic_unit=(1.0, "T")periodicity: A tuple of booleans that determines whether the data will be treated as periodic along each axisgeometry: The geometry of the dataset, can becartesian,cylindrical,polar,spherical,geographicorspectral_cubedefault_species_fields: if set toionizedorneutral, default species fields are accordingly created for H and He which also set mean molecular weightaxis_order: The order of the axes in the data array, e.g.("z", "y", "x")with cartesian geometrycell_widths: If set, specify the cell widths along each dimension. Must be consistent with thedomain_dimensionsargumentparameters: A dictionary of dataset parameters, , useful for storing dataset metadatadataset_name: The name of the dataset. Stream datasets will use this value in place of a filename (in image prefixing, etc.)
This example creates a yt-native dataset ds that will treat your array as a density field in cubic domain of 3 Mpc edge size and simultaneously divide the domain into nprocs = 64 chunks, so that you can take advantage of the underlying parallelism.
The optional unit keyword arguments allow for the default units of the dataset to be set. They can be: * A string, e.g. length_unit="Mpc" * A tuple, e.g. mass_unit=(1.0e14, "Msun") * A floating-point value, e.g. time_unit=3.1557e13
In the latter case, the unit is assumed to be cgs.
The resulting ds functions exactly like a dataset like any other yt can handle–it can be sliced, and we can show the grid boundaries:
[4]:
slc = yt.SlicePlot(ds, "z", ("gas", "density"))
slc.set_cmap(("gas", "density"), "Blues")
slc.annotate_grids(cmap=None)
slc.show()
Particle fields are detected as one-dimensional fields. Particle fields are then added as one-dimensional arrays in a similar manner as the three-dimensional grid fields:
[5]:
posx_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=10000)
posy_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=10000)
posz_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=10000)
data = {
"density": (prng.random(size=(64, 64, 64)), "Msun/kpc**3"),
"particle_position_x": (posx_arr, "code_length"),
"particle_position_y": (posy_arr, "code_length"),
"particle_position_z": (posz_arr, "code_length"),
}
bbox = np.array([[-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5]])
ds = yt.load_uniform_grid(
data,
data["density"][0].shape,
length_unit=(1.0, "Mpc"),
mass_unit=(1.0, "Msun"),
bbox=bbox,
nprocs=4,
)
In this example only the particle position fields have been assigned. If no particle arrays are supplied, then the number of particles is assumed to be zero. Take a slice, and overlay particle positions:
[6]:
slc = yt.SlicePlot(ds, "z", ("gas", "density"))
slc.set_cmap(("gas", "density"), "Blues")
slc.annotate_particles(0.25, p_size=12.0, col="Red")
slc.show()
HDF5 data¶
HDF5 is a convenient format to store data. If you have unigrid data stored in an HDF5 file, it is possible to load it into memory and then use load_uniform_grid to get it into yt:
[7]:
from os.path import join
import h5py
from yt.config import ytcfg
data_dir = ytcfg.get("yt", "test_data_dir")
from yt.utilities.physical_ratios import cm_per_kpc
f = h5py.File(
join(data_dir, "UnigridData", "turb_vels.h5"), "r"
) # Read-only access to the file
The HDF5 file handle’s keys correspond to the datasets stored in the file:
[8]:
print(f.keys())
<KeysViewHDF5 ['Bx', 'By', 'Bz', 'Density', 'MagneticEnergy', 'Temperature', 'turb_x-velocity', 'turb_y-velocity', 'turb_z-velocity', 'x-velocity', 'y-velocity', 'z-velocity']>
We need to add some unit information. It may be stored in the file somewhere, or we may know it from another source. In this case, the units are simply cgs:
[9]:
units = [
"gauss",
"gauss",
"gauss",
"g/cm**3",
"erg/cm**3",
"K",
"cm/s",
"cm/s",
"cm/s",
"cm/s",
"cm/s",
"cm/s",
]
We can iterate over the items in the file handle and the units to get the data into a dictionary, which we will then load:
[10]:
data = {k: (v[()], u) for (k, v), u in zip(f.items(), units)}
bbox = np.array([[-0.5, 0.5], [-0.5, 0.5], [-0.5, 0.5]])
[11]:
ds = yt.load_uniform_grid(
data,
data["Density"][0].shape,
length_unit=250.0 * cm_per_kpc,
bbox=bbox,
nprocs=8,
periodicity=(False, False, False),
)
In this case, the data came from a simulation which was 250 kpc on a side. An example projection of two fields:
[12]:
prj = yt.ProjectionPlot(
ds, "z", ["z-velocity", "Temperature", "Bx"], weight_field="Density"
)
prj.set_log("z-velocity", False)
prj.set_log("Bx", False)
prj.show()
Volume Rendering Loaded Data¶
Volume rendering requires defining a TransferFunction to map data to color and opacity and a camera to create a viewport and render the image.
[13]:
# Find the min and max of the field
mi, ma = ds.all_data().quantities.extrema("Temperature")
# Reduce the dynamic range
mi = mi.value + 1.5e7
ma = ma.value - 0.81e7
Define the properties and size of the camera viewport:
[14]:
# Choose a vector representing the viewing direction.
L = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
# Define the center of the camera to be the domain center
c = ds.domain_center[0]
# Define the width of the image
W = 1.5 * ds.domain_width[0]
# Define the number of pixels to render
Npixels = 512
Create a camera object and
[15]:
sc = yt.create_scene(ds, "Temperature")
dd = ds.all_data()
source = sc[0]
source.log_field = False
tf = yt.ColorTransferFunction((mi, ma), grey_opacity=False)
tf.map_to_colormap(mi, ma, scale=15.0, colormap="cmyt.algae")
source.set_transfer_function(tf)
sc.add_source(source)
cam = sc.add_camera()
cam.width = W
cam.center = c
cam.normal_vector = L
cam.north_vector = [0, 0, 1]
[16]:
sc.show(sigma_clip=4)
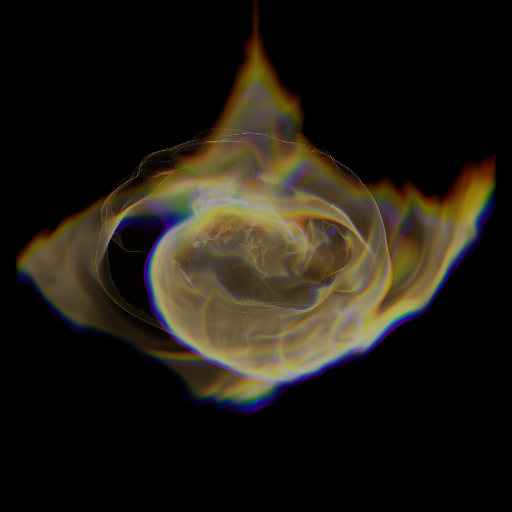
FITS image data¶
The FITS file format is a common astronomical format for 2-D images, but it can store three-dimensional data as well. The AstroPy project has modules for FITS reading and writing.
[17]:
import astropy.io.fits as pyfits
Using pyfits we can open a FITS file. If we call info() on the file handle, we can figure out some information about the file’s contents. The file in this example has a primary HDU (header-data-unit) with no data, and three HDUs with 3-D data. In this case, the data consists of three velocity fields:
[18]:
f = pyfits.open(join(data_dir, "UnigridData", "velocity_field_20.fits"))
f.info()
Filename: /mnt/yt/UnigridData/velocity_field_20.fits
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 X-VELOCITY 1 PrimaryHDU 25 (200, 200, 200) float64
1 Y-VELOCITY 1 ImageHDU 26 (200, 200, 200) float64
2 Z-VELOCITY 1 ImageHDU 26 (200, 200, 200) float64
We can put it into a dictionary in the same way as before, but we slice the file handle f so that we don’t use the PrimaryHDU. hdu.name is the field name and hdu.data is the actual data. Each of these velocity fields is in km/s. We can check that we got the correct fields.
[19]:
data = {}
for hdu in f:
name = hdu.name.lower()
data[name] = (hdu.data, "km/s")
print(data.keys())
dict_keys(['x-velocity', 'y-velocity', 'z-velocity'])
The velocity field names in this case are slightly different than the standard yt field names for velocity fields, so we will reassign the field names:
[20]:
data["velocity_x"] = data.pop("x-velocity")
data["velocity_y"] = data.pop("y-velocity")
data["velocity_z"] = data.pop("z-velocity")
Now we load the data into yt. Let’s assume that the box size is a Mpc. Since these are velocity fields, we can overlay velocity vectors on slices, just as if we had loaded in data from a supported code.
[21]:
ds = yt.load_uniform_grid(data, data["velocity_x"][0].shape, length_unit=(1.0, "Mpc"))
slc = yt.SlicePlot(
ds, "x", [("gas", "velocity_x"), ("gas", "velocity_y"), ("gas", "velocity_z")]
)
for ax in "xyz":
slc.set_log(("gas", f"velocity_{ax}"), False)
slc.annotate_velocity()
slc.show()
Generic AMR Data¶
In a similar fashion to unigrid data, data gridded into rectangular patches at varying levels of resolution may also be loaded into yt. In this case, a list of grid dictionaries should be provided, with the requisite information about each grid’s properties. This example sets up two grids: a top-level grid (level == 0) covering the entire domain and a subgrid at level == 1.
[22]:
grid_data = [
{
"left_edge": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
"right_edge": [1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
"level": 0,
"dimensions": [32, 32, 32],
},
{
"left_edge": [0.25, 0.25, 0.25],
"right_edge": [0.75, 0.75, 0.75],
"level": 1,
"dimensions": [32, 32, 32],
},
]
We’ll just fill each grid with random density data, with a scaling with the grid refinement level.
[23]:
for g in grid_data:
g["density"] = (prng.random(g["dimensions"]) * 2 ** g["level"], "g/cm**3")
Particle fields are supported by adding 1-dimensional arrays to each grid. If a grid has no particles, the particle fields still have to be defined since they are defined elsewhere; set them to empty NumPy arrays:
[24]:
grid_data[0]["particle_position_x"] = (
np.array([]),
"code_length",
) # No particles, so set empty arrays
grid_data[0]["particle_position_y"] = (np.array([]), "code_length")
grid_data[0]["particle_position_z"] = (np.array([]), "code_length")
grid_data[1]["particle_position_x"] = (
prng.uniform(low=0.25, high=0.75, size=1000),
"code_length",
)
grid_data[1]["particle_position_y"] = (
prng.uniform(low=0.25, high=0.75, size=1000),
"code_length",
)
grid_data[1]["particle_position_z"] = (
prng.uniform(low=0.25, high=0.75, size=1000),
"code_length",
)
Then, call load_amr_grids:
[25]:
ds = yt.load_amr_grids(grid_data, [32, 32, 32])
load_amr_grids also takes the same keywords bbox and sim_time as load_uniform_grid. We could have also specified the length, time, velocity, and mass units in the same manner as before. Let’s take a slice:
[26]:
slc = yt.SlicePlot(ds, "z", ("gas", "density"))
slc.annotate_particles(0.25, p_size=15.0, col="Pink")
slc.show()
Species fields¶
One can also supply species fields to a stream dataset, in the form of mass fractions. These will then be used to generate derived fields for mass, number, and nuclei densities of the separate species. The naming conventions for the mass fractions should correspond to the format specified in the yt documentation for species fields.
[27]:
arr = prng.random(size=(64, 64, 64))
data = {
"density": (arr, "g/cm**3"),
"H_p0_fraction": (0.37 * np.ones_like(arr), "dimensionless"),
"H_p1_fraction": (0.37 * np.ones_like(arr), "dimensionless"),
"He_fraction": (0.24 * np.ones_like(arr), "dimensionless"),
"CO_fraction": (0.02 * np.ones_like(arr), "dimensionless"),
}
bbox = np.array([[-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5]])
ds = yt.load_uniform_grid(data, arr.shape, length_unit="Mpc", bbox=bbox, nprocs=64)
dd = ds.all_data()
print(dd.mean(("gas", "CO_density")))
print(dd.min(("gas", "H_nuclei_density")))
print(dd.max(("gas", "He_number_density")))
0.010015091445398647 g/(cm**3*dimensionless)
5.52674242786293e+16 cm**(-3)
3.610929091043805e+22 cm**(-3)
Multiple Particle Types¶
For both uniform grid data and AMR data, one can specify particle fields with multiple types if the particle field names are given as field tuples instead of strings (the default particle type is "io"):
[28]:
posxr_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=10000)
posyr_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=10000)
poszr_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=10000)
posxb_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=20000)
posyb_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=20000)
poszb_arr = prng.uniform(low=-1.5, high=1.5, size=20000)
data = {
("gas", "density"): (prng.random(size=(64, 64, 64)), "Msun/kpc**3"),
("red", "particle_position_x"): (posxr_arr, "code_length"),
("red", "particle_position_y"): (posyr_arr, "code_length"),
("red", "particle_position_z"): (poszr_arr, "code_length"),
("blue", "particle_position_x"): (posxb_arr, "code_length"),
("blue", "particle_position_y"): (posyb_arr, "code_length"),
("blue", "particle_position_z"): (poszb_arr, "code_length"),
}
bbox = np.array([[-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5]])
ds = yt.load_uniform_grid(
data,
data["gas", "density"][0].shape,
length_unit=(1.0, "Mpc"),
mass_unit=(1.0, "Msun"),
bbox=bbox,
nprocs=4,
)
We can now see we have multiple particle types:
[29]:
dd = ds.all_data()
print(ds.particle_types)
print(dd["red", "particle_position_x"].size)
print(dd["blue", "particle_position_x"].size)
print(dd["all", "particle_position_x"].size)
('red', 'blue', 'all')
10000
20000
30000
Caveats for Loading Generic Array Data¶
Particles may be difficult to integrate.
Data must already reside in memory before loading it in to yt, whether it is generated at runtime or loaded from disk.
Some functions may behave oddly, and parallelism will be disappointing or non-existent in most cases.
No consistency checks are performed on the hierarchy
Consistency between particle positions and grids is not checked;
load_amr_gridsassumes that particle positions associated with one grid are not bounded within another grid at a higher level, so this must be ensured by the user prior to loading the grid data.